
Integrating AI and 5G, A convergence of virtual, augmented, and mixed realities is redefining industries and positioning XR as a cornerstone of India’s digital transformation.
Extended reality (XR), an umbrella term encompassing virtual reality (VR), augmented reality (AR), and mixed reality (MR), is rapidly transforming the way we interact with the digital and physical worlds. As hardware becomes more sophisticated and artificial intelligence (AI) integrates seamlessly with XR, the technology is poised to be a cornerstone of the future.
Infrastructure Involved
The infrastructure required for XR consists of several key components that enable immersive digital experiences. At the core are high-performance computing systems, including powerful processors, graphics processing units (GPUs), and cloud computing services that handle real-time rendering and data processing.
Hardware devices such as VR headsets, AR glasses, motion-tracking sensors, and haptic feedback systems form the interface between users and digital environments. Network infrastructure, particularly high-speed internet and 5G connectivity, plays a crucial role. Data storage solutions, whether cloud-based or on-premise, are necessary to manage vast amounts of spatial data and AI-driven enhancements.
XR infrastructure also depends on robust software ecosystems. Development platforms like Unity and Unreal Engine provide tools to create immersive experiences, while AI and machine learning enhance realism and interactivity. Edge computing is increasingly adopted to process data closer to users, reducing latency and improving responsiveness. Security infrastructure is vital to protect sensitive user data and prevent cyber threats in virtual environments.
The development of standard protocols and interoperability frameworks ensures seamless integration of XR applications across industries.
How does XR enhance AR, VR, and MR?
XR serves as an overarching framework that enhances AR, VR, and MR by integrating technologies such as AI, 5G connectivity, and cloud computing. In AR, XR improves real-world overlays through enhanced object recognition, spatial mapping, and real-time data processing. AI enables adaptive content that responds intelligently to user behaviour and surroundings.
In VR, XR refines sensory feedback, improves haptic technology, and reduces latency for more realistic simulations. XR-driven VR enables highly detailed environments for training, gaming, and remote collaboration. In MR, XR advances spatial computing, allowing digital objects to interact dynamically with the real world, which is beneficial in sectors like engineering and manufacturing, where 3D models can be visualised overlaid onto real-world machinery.
By integrating XR technologies, AR, VR, and MR become more efficient, adaptive, and scalable.
Key Players involved
The XR industry is driven by several key players, including global tech giants and innovative startups. Companies like Meta (formerly Facebook), Microsoft, Google, and Apple are at the forefront, developing cutting-edge XR hardware and software. Meta’s Quest headsets dominate the VR market, while Microsoft’s HoloLens leads in MR applications for enterprise solutions. Google continues to push AR experiences with its Google Lens and ARCore platform, while Apple is advancing AR with its Vision Pro headset and ARKit for developers.
Meanwhile, HTC Vive and Sony PlayStation VR focus on immersive gaming and entertainment, while Qualcomm develops XR-specific chipsets to power mobile and wearable devices. In India, startups such as Whodat, Scapic, and SmartVizX are driving innovation in AR, VR, and MR applications across various industries, including real estate, retail, and education. Magic Leap and Unity Technologies provide software tools that empower developers to create immersive XR experiences.
Business scenario of XR in India
India’s XR market is experiencing rapid growth, driven by technological advancements and increased adoption across various sectors. The market expanded from $0.34 billion in 2017 to $1.83 billion in 2020, reflecting a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 75%. Projections indicate that this growth trajectory will continue, with an expected CAGR of 38.29%, potentially reaching $14.07 billion by 2027. This surge is attributed to factors such as widespread smartphone usage, a burgeoning tech-savvy population, and the integration of XR technologies in sectors like education, gaming, and retail.
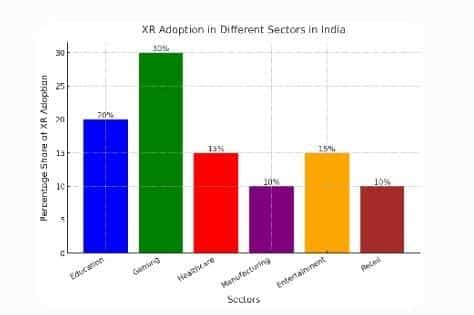
Several multinational corporations are actively implementing XR solutions within India. Siemens Healthineers, for instance, has developed an immersive virtual reality training program in partnership with PrecisionOS, enabling surgeons and technicians to practice procedures using the mobile 3D C-arm Cios Spin in a virtual environment. While specific XR initiatives by ABB and Intel in India are not detailed in the available sources, these companies have globally recognised the potential of XR. ABB has been involved in XR applications within manufacturing contexts, enhancing human-machine interactions through digital twins. Intel showcases various case studies highlighting XR integration to drive innovation and operational efficiency.
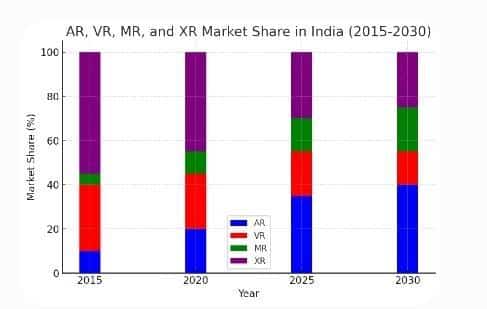
XR is rapidly transforming industries in India through its applications in training, collaboration, and real-world interaction. With adoption growing across education, healthcare, manufacturing, gaming, and retail, and with continued investment in AI, 5G, and cloud computing, India is emerging as a significant player in the global XR ecosystem. The outlook is strong, with expanding opportunities for innovation, economic growth, and digital transformation.
References:
- Intel
- Siemens Healthineers
- mdpi.com
Author: Vinayak Ramachandra Adkoli. The author holds a BE degree in Industrial Production and has been a lecturer in three different polytechnics for ten years. He is also a freelance writer and cartoonist.










